 - **Dockerfile:** GPU image recommended for training.
- **Dockerfile-arm64:** Optimized for ARM64 architecture, allowing deployment on devices like Raspberry Pi and other ARM64-based platforms.
- **Dockerfile-cpu:** Ubuntu-based CPU-only version suitable for inference and environments without GPUs.
- **Dockerfile-jetson:** Tailored for NVIDIA Jetson devices, integrating GPU support optimized for these platforms.
- **Dockerfile-python:** Minimal image with just Python and necessary dependencies, ideal for lightweight applications and development.
- **Dockerfile-conda:** Based on Miniconda3 with conda installation of ultralytics package.
Below are the commands to get the latest image and execute it:
```bash
# Set image name as a variable
t=ultralytics/ultralytics:latest
# Pull the latest ultralytics image from Docker Hub
sudo docker pull $t
# Run the ultralytics image in a container with GPU support
sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus all $t # all GPUs
sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus '"device=2,3"' $t # specify GPUs
```
The above command initializes a Docker container with the latest `ultralytics` image. The `-it` flag assigns a pseudo-TTY and maintains stdin open, enabling you to interact with the container. The `--ipc=host` flag sets the IPC (Inter-Process Communication) namespace to the host, which is essential for sharing memory between processes. The `--gpus all` flag enables access to all available GPUs inside the container, which is crucial for tasks that require GPU computation.
Note: To work with files on your local machine within the container, use Docker volumes for mounting a local directory into the container:
```bash
# Mount local directory to a directory inside the container
sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus all -v /path/on/host:/path/in/container $t
```
Alter `/path/on/host` with the directory path on your local machine, and `/path/in/container` with the desired path inside the Docker container for accessibility.
For advanced Docker usage, feel free to explore the [Ultralytics Docker Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/guides/docker-quickstart/).
See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/requirements.txt) file for a list of dependencies. Note that all examples above install all required dependencies.
- **Dockerfile:** GPU image recommended for training.
- **Dockerfile-arm64:** Optimized for ARM64 architecture, allowing deployment on devices like Raspberry Pi and other ARM64-based platforms.
- **Dockerfile-cpu:** Ubuntu-based CPU-only version suitable for inference and environments without GPUs.
- **Dockerfile-jetson:** Tailored for NVIDIA Jetson devices, integrating GPU support optimized for these platforms.
- **Dockerfile-python:** Minimal image with just Python and necessary dependencies, ideal for lightweight applications and development.
- **Dockerfile-conda:** Based on Miniconda3 with conda installation of ultralytics package.
Below are the commands to get the latest image and execute it:
```bash
# Set image name as a variable
t=ultralytics/ultralytics:latest
# Pull the latest ultralytics image from Docker Hub
sudo docker pull $t
# Run the ultralytics image in a container with GPU support
sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus all $t # all GPUs
sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus '"device=2,3"' $t # specify GPUs
```
The above command initializes a Docker container with the latest `ultralytics` image. The `-it` flag assigns a pseudo-TTY and maintains stdin open, enabling you to interact with the container. The `--ipc=host` flag sets the IPC (Inter-Process Communication) namespace to the host, which is essential for sharing memory between processes. The `--gpus all` flag enables access to all available GPUs inside the container, which is crucial for tasks that require GPU computation.
Note: To work with files on your local machine within the container, use Docker volumes for mounting a local directory into the container:
```bash
# Mount local directory to a directory inside the container
sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus all -v /path/on/host:/path/in/container $t
```
Alter `/path/on/host` with the directory path on your local machine, and `/path/in/container` with the desired path inside the Docker container for accessibility.
For advanced Docker usage, feel free to explore the [Ultralytics Docker Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/guides/docker-quickstart/).
See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/requirements.txt) file for a list of dependencies. Note that all examples above install all required dependencies.
Watch: Ultralytics YOLO Quick Start Guide
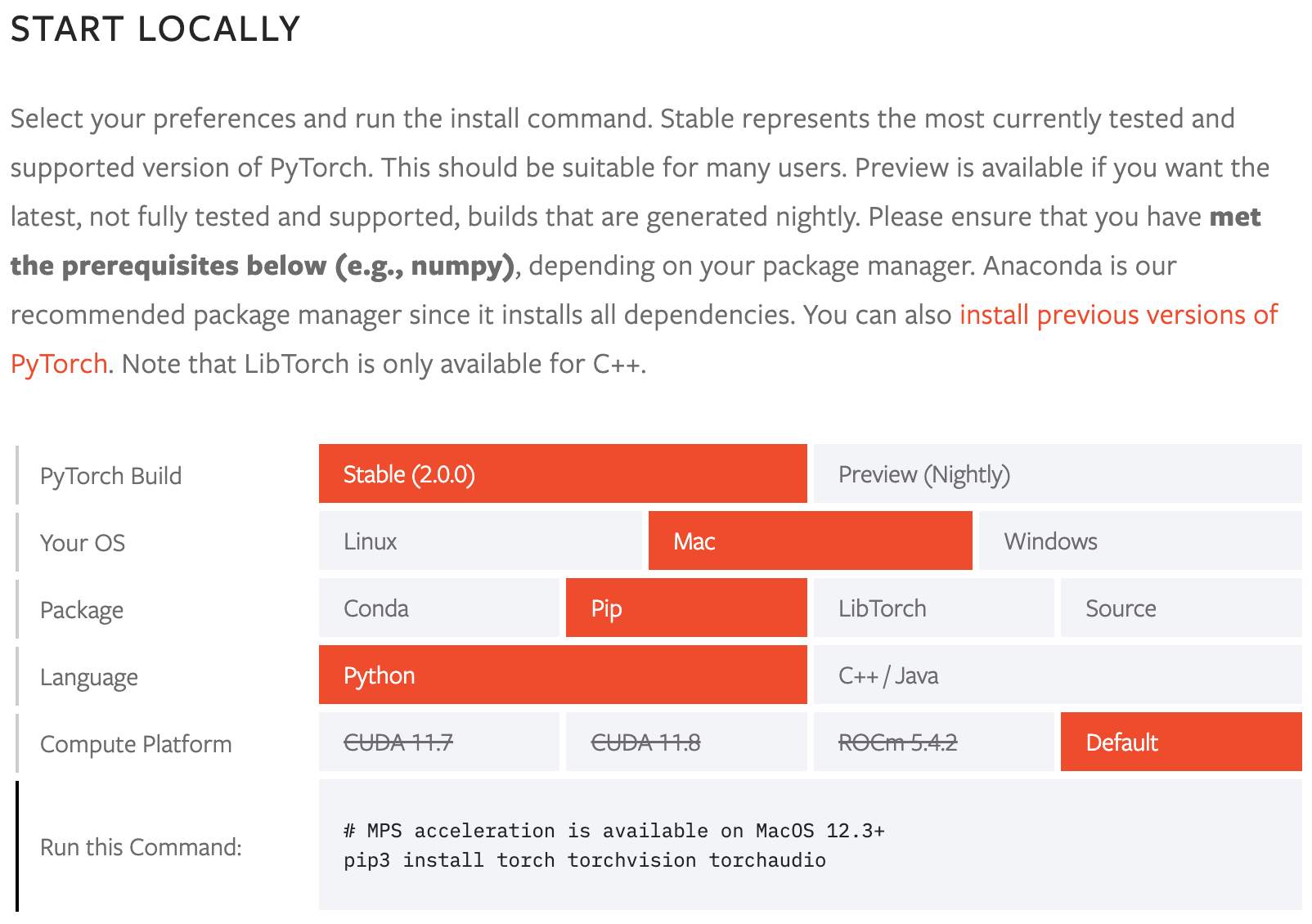 ## Use Ultralytics with CLI
The Ultralytics command line interface (CLI) allows for simple single-line commands without the need for a Python environment. CLI requires no customization or Python code. You can simply run all tasks from the terminal with the `yolo` command. Check out the [CLI Guide](usage/cli.md) to learn more about using YOLOv8 from the command line.
!!! Example
=== "Syntax"
Ultralytics `yolo` commands use the following syntax:
```bash
yolo TASK MODE ARGS
```
- `TASK` (optional) is one of ([detect](tasks/detect.md), [segment](tasks/segment.md), [classify](tasks/classify.md), [pose](tasks/pose.md))
- `MODE` (required) is one of ([train](modes/train.md), [val](modes/val.md), [predict](modes/predict.md), [export](modes/export.md), [track](modes/track.md))
- `ARGS` (optional) are `arg=value` pairs like `imgsz=640` that override defaults.
See all `ARGS` in the full [Configuration Guide](usage/cfg.md) or with the `yolo cfg` CLI command.
=== "Train"
Train a detection model for 10 epochs with an initial learning_rate of 0.01
```bash
yolo train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.pt epochs=10 lr0=0.01
```
=== "Predict"
Predict a YouTube video using a pretrained segmentation model at image size 320:
```bash
yolo predict model=yolov8n-seg.pt source='https://youtu.be/LNwODJXcvt4' imgsz=320
```
=== "Val"
Val a pretrained detection model at batch-size 1 and image size 640:
```bash
yolo val model=yolov8n.pt data=coco128.yaml batch=1 imgsz=640
```
=== "Export"
Export a YOLOv8n classification model to ONNX format at image size 224 by 128 (no TASK required)
```bash
yolo export model=yolov8n-cls.pt format=onnx imgsz=224,128
```
=== "Special"
Run special commands to see version, view settings, run checks and more:
```bash
yolo help
yolo checks
yolo version
yolo settings
yolo copy-cfg
yolo cfg
```
!!! Warning "Warning"
Arguments must be passed as `arg=val` pairs, split by an equals `=` sign and delimited by spaces between pairs. Do not use `--` argument prefixes or commas `,` between arguments.
- `yolo predict model=yolov8n.pt imgsz=640 conf=0.25` ✅
- `yolo predict model yolov8n.pt imgsz 640 conf 0.25` ❌ (missing `=`)
- `yolo predict model=yolov8n.pt, imgsz=640, conf=0.25` ❌ (do not use `,`)
- `yolo predict --model yolov8n.pt --imgsz 640 --conf 0.25` ❌ (do not use `--`)
[CLI Guide](usage/cli.md){ .md-button }
## Use Ultralytics with Python
YOLOv8's Python interface allows for seamless integration into your Python projects, making it easy to load, run, and process the model's output. Designed with simplicity and ease of use in mind, the Python interface enables users to quickly implement object detection, segmentation, and classification in their projects. This makes YOLOv8's Python interface an invaluable tool for anyone looking to incorporate these functionalities into their Python projects.
For example, users can load a model, train it, evaluate its performance on a validation set, and even export it to ONNX format with just a few lines of code. Check out the [Python Guide](usage/python.md) to learn more about using YOLOv8 within your Python projects.
!!! Example
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Create a new YOLO model from scratch
model = YOLO('yolov8n.yaml')
# Load a pretrained YOLO model (recommended for training)
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
# Train the model using the 'coco128.yaml' dataset for 3 epochs
results = model.train(data='coco128.yaml', epochs=3)
# Evaluate the model's performance on the validation set
results = model.val()
# Perform object detection on an image using the model
results = model('https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg')
# Export the model to ONNX format
success = model.export(format='onnx')
```
[Python Guide](usage/python.md){.md-button .md-button--primary}
## Ultralytics Settings
The Ultralytics library provides a powerful settings management system to enable fine-grained control over your experiments. By making use of the `SettingsManager` housed within the `ultralytics.utils` module, users can readily access and alter their settings. These are stored in a YAML file and can be viewed or modified either directly within the Python environment or via the Command-Line Interface (CLI).
### Inspecting Settings
To gain insight into the current configuration of your settings, you can view them directly:
!!! Example "View settings"
=== "Python"
You can use Python to view your settings. Start by importing the `settings` object from the `ultralytics` module. Print and return settings using the following commands:
```python
from ultralytics import settings
# View all settings
print(settings)
# Return a specific setting
value = settings['runs_dir']
```
=== "CLI"
Alternatively, the command-line interface allows you to check your settings with a simple command:
```bash
yolo settings
```
### Modifying Settings
Ultralytics allows users to easily modify their settings. Changes can be performed in the following ways:
!!! Example "Update settings"
=== "Python"
Within the Python environment, call the `update` method on the `settings` object to change your settings:
```python
from ultralytics import settings
# Update a setting
settings.update({'runs_dir': '/path/to/runs'})
# Update multiple settings
settings.update({'runs_dir': '/path/to/runs', 'tensorboard': False})
# Reset settings to default values
settings.reset()
```
=== "CLI"
If you prefer using the command-line interface, the following commands will allow you to modify your settings:
```bash
# Update a setting
yolo settings runs_dir='/path/to/runs'
# Update multiple settings
yolo settings runs_dir='/path/to/runs' tensorboard=False
# Reset settings to default values
yolo settings reset
```
### Understanding Settings
The table below provides an overview of the settings available for adjustment within Ultralytics. Each setting is outlined along with an example value, the data type, and a brief description.
| Name | Example Value | Data Type | Description |
|--------------------|-----------------------|-----------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| `settings_version` | `'0.0.4'` | `str` | Ultralytics _settings_ version (different from Ultralytics [pip](https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/) version) |
| `datasets_dir` | `'/path/to/datasets'` | `str` | The directory where the datasets are stored |
| `weights_dir` | `'/path/to/weights'` | `str` | The directory where the model weights are stored |
| `runs_dir` | `'/path/to/runs'` | `str` | The directory where the experiment runs are stored |
| `uuid` | `'a1b2c3d4'` | `str` | The unique identifier for the current settings |
| `sync` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to sync analytics and crashes to HUB |
| `api_key` | `''` | `str` | Ultralytics HUB [API Key](https://hub.ultralytics.com/settings?tab=api+keys) |
| `clearml` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use ClearML logging |
| `comet` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use [Comet ML](https://bit.ly/yolov8-readme-comet) for experiment tracking and visualization |
| `dvc` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use [DVC for experiment tracking](https://dvc.org/doc/dvclive/ml-frameworks/yolo) and version control |
| `hub` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use [Ultralytics HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com) integration |
| `mlflow` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use MLFlow for experiment tracking |
| `neptune` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use Neptune for experiment tracking |
| `raytune` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use Ray Tune for hyperparameter tuning |
| `tensorboard` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use TensorBoard for visualization |
| `wandb` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use Weights & Biases logging |
As you navigate through your projects or experiments, be sure to revisit these settings to ensure that they are optimally configured for your needs.
## Use Ultralytics with CLI
The Ultralytics command line interface (CLI) allows for simple single-line commands without the need for a Python environment. CLI requires no customization or Python code. You can simply run all tasks from the terminal with the `yolo` command. Check out the [CLI Guide](usage/cli.md) to learn more about using YOLOv8 from the command line.
!!! Example
=== "Syntax"
Ultralytics `yolo` commands use the following syntax:
```bash
yolo TASK MODE ARGS
```
- `TASK` (optional) is one of ([detect](tasks/detect.md), [segment](tasks/segment.md), [classify](tasks/classify.md), [pose](tasks/pose.md))
- `MODE` (required) is one of ([train](modes/train.md), [val](modes/val.md), [predict](modes/predict.md), [export](modes/export.md), [track](modes/track.md))
- `ARGS` (optional) are `arg=value` pairs like `imgsz=640` that override defaults.
See all `ARGS` in the full [Configuration Guide](usage/cfg.md) or with the `yolo cfg` CLI command.
=== "Train"
Train a detection model for 10 epochs with an initial learning_rate of 0.01
```bash
yolo train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.pt epochs=10 lr0=0.01
```
=== "Predict"
Predict a YouTube video using a pretrained segmentation model at image size 320:
```bash
yolo predict model=yolov8n-seg.pt source='https://youtu.be/LNwODJXcvt4' imgsz=320
```
=== "Val"
Val a pretrained detection model at batch-size 1 and image size 640:
```bash
yolo val model=yolov8n.pt data=coco128.yaml batch=1 imgsz=640
```
=== "Export"
Export a YOLOv8n classification model to ONNX format at image size 224 by 128 (no TASK required)
```bash
yolo export model=yolov8n-cls.pt format=onnx imgsz=224,128
```
=== "Special"
Run special commands to see version, view settings, run checks and more:
```bash
yolo help
yolo checks
yolo version
yolo settings
yolo copy-cfg
yolo cfg
```
!!! Warning "Warning"
Arguments must be passed as `arg=val` pairs, split by an equals `=` sign and delimited by spaces between pairs. Do not use `--` argument prefixes or commas `,` between arguments.
- `yolo predict model=yolov8n.pt imgsz=640 conf=0.25` ✅
- `yolo predict model yolov8n.pt imgsz 640 conf 0.25` ❌ (missing `=`)
- `yolo predict model=yolov8n.pt, imgsz=640, conf=0.25` ❌ (do not use `,`)
- `yolo predict --model yolov8n.pt --imgsz 640 --conf 0.25` ❌ (do not use `--`)
[CLI Guide](usage/cli.md){ .md-button }
## Use Ultralytics with Python
YOLOv8's Python interface allows for seamless integration into your Python projects, making it easy to load, run, and process the model's output. Designed with simplicity and ease of use in mind, the Python interface enables users to quickly implement object detection, segmentation, and classification in their projects. This makes YOLOv8's Python interface an invaluable tool for anyone looking to incorporate these functionalities into their Python projects.
For example, users can load a model, train it, evaluate its performance on a validation set, and even export it to ONNX format with just a few lines of code. Check out the [Python Guide](usage/python.md) to learn more about using YOLOv8 within your Python projects.
!!! Example
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Create a new YOLO model from scratch
model = YOLO('yolov8n.yaml')
# Load a pretrained YOLO model (recommended for training)
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
# Train the model using the 'coco128.yaml' dataset for 3 epochs
results = model.train(data='coco128.yaml', epochs=3)
# Evaluate the model's performance on the validation set
results = model.val()
# Perform object detection on an image using the model
results = model('https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg')
# Export the model to ONNX format
success = model.export(format='onnx')
```
[Python Guide](usage/python.md){.md-button .md-button--primary}
## Ultralytics Settings
The Ultralytics library provides a powerful settings management system to enable fine-grained control over your experiments. By making use of the `SettingsManager` housed within the `ultralytics.utils` module, users can readily access and alter their settings. These are stored in a YAML file and can be viewed or modified either directly within the Python environment or via the Command-Line Interface (CLI).
### Inspecting Settings
To gain insight into the current configuration of your settings, you can view them directly:
!!! Example "View settings"
=== "Python"
You can use Python to view your settings. Start by importing the `settings` object from the `ultralytics` module. Print and return settings using the following commands:
```python
from ultralytics import settings
# View all settings
print(settings)
# Return a specific setting
value = settings['runs_dir']
```
=== "CLI"
Alternatively, the command-line interface allows you to check your settings with a simple command:
```bash
yolo settings
```
### Modifying Settings
Ultralytics allows users to easily modify their settings. Changes can be performed in the following ways:
!!! Example "Update settings"
=== "Python"
Within the Python environment, call the `update` method on the `settings` object to change your settings:
```python
from ultralytics import settings
# Update a setting
settings.update({'runs_dir': '/path/to/runs'})
# Update multiple settings
settings.update({'runs_dir': '/path/to/runs', 'tensorboard': False})
# Reset settings to default values
settings.reset()
```
=== "CLI"
If you prefer using the command-line interface, the following commands will allow you to modify your settings:
```bash
# Update a setting
yolo settings runs_dir='/path/to/runs'
# Update multiple settings
yolo settings runs_dir='/path/to/runs' tensorboard=False
# Reset settings to default values
yolo settings reset
```
### Understanding Settings
The table below provides an overview of the settings available for adjustment within Ultralytics. Each setting is outlined along with an example value, the data type, and a brief description.
| Name | Example Value | Data Type | Description |
|--------------------|-----------------------|-----------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| `settings_version` | `'0.0.4'` | `str` | Ultralytics _settings_ version (different from Ultralytics [pip](https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/) version) |
| `datasets_dir` | `'/path/to/datasets'` | `str` | The directory where the datasets are stored |
| `weights_dir` | `'/path/to/weights'` | `str` | The directory where the model weights are stored |
| `runs_dir` | `'/path/to/runs'` | `str` | The directory where the experiment runs are stored |
| `uuid` | `'a1b2c3d4'` | `str` | The unique identifier for the current settings |
| `sync` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to sync analytics and crashes to HUB |
| `api_key` | `''` | `str` | Ultralytics HUB [API Key](https://hub.ultralytics.com/settings?tab=api+keys) |
| `clearml` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use ClearML logging |
| `comet` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use [Comet ML](https://bit.ly/yolov8-readme-comet) for experiment tracking and visualization |
| `dvc` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use [DVC for experiment tracking](https://dvc.org/doc/dvclive/ml-frameworks/yolo) and version control |
| `hub` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use [Ultralytics HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com) integration |
| `mlflow` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use MLFlow for experiment tracking |
| `neptune` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use Neptune for experiment tracking |
| `raytune` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use Ray Tune for hyperparameter tuning |
| `tensorboard` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use TensorBoard for visualization |
| `wandb` | `True` | `bool` | Whether to use Weights & Biases logging |
As you navigate through your projects or experiments, be sure to revisit these settings to ensure that they are optimally configured for your needs.